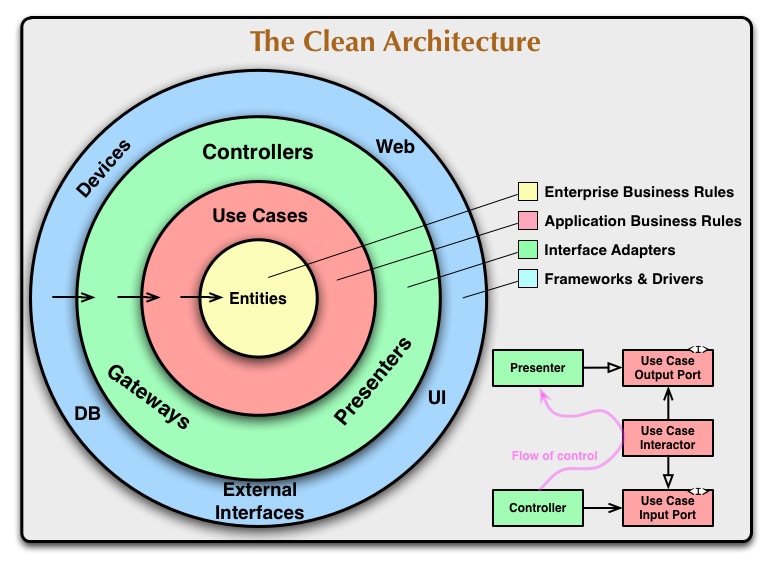
This is implementation clean architecture by Uncle Bob. We can implementation this project to make application with many module and component. First we must prepare some library for supporting our project like injector, api consume like dio and many other library we must intall it. In this case I made a facebook clone with rest API and you can clone it anytime and feel free to wait for my update app to make sure the app works properly.
Clean Architecture combines a group of practices that produce systems with the following characteristics:
✅ Testable
✅ UI-independent (the UI can easily be changed without changing the system)
✅ Independent of databases, frameworks, external agencies, and libraries
The dependency rule is the overriding rule that makes Clean Architecture work. It says that nothing in an inner circle should depend on anything in an outer circle. In particular, application and business rules shouldn’t depend on the UI, database, presenters, and so on. These rules allow us to build systems that are simpler to maintain, as changes in outer circles won’t impact inner ones.
The Domain module defines the business logic of the application. It is a module that is independent from the development platform i.e. it is written purely in the programming language and does not contain any elements from the platform. The reason for that is that Domain should only be concerned with the business logic of the application, not with the implementation details. This also allows for easy migration between platforms, should any issues arise.
✅ Enterprise-wide business rules
✅ Made up of classes that can contain methods
✅ Business objects of the application
✅ Used application-wide
✅ Least likely to change when something in the application changes
✅ Application-specific business rules
✅ Encapsulate all the usecases of the application
✅ Orchestrate the flow of data throughout the app
✅ Should not be affected by any UI changes whatsoever
✅ Might change if the functionality and flow of application change
✅ Abstract classes that define the expected functionality of outer layers
✅ Are not aware of outer layers, simply define expected functionality
✅ E.g. The Login usecase expects a Repository that has login functionality
✅ Passed to Usecases from outer layers
✅ Domain represents the inner-most layer. Therefore, it the most abstract layer in the architecture.
You can clone this library using :
git clone https://github.com/imamabdulazis/FlutterCleanArchitecture.gitflutter clean; flutter pub getWe need some library to make our apps is more simple code and clean. This is some library and you can click to install from pub dev.
| Library | Usability | Star |
|---|---|---|
| dartz | Data Handling |  |
| dio | Http client |  |
| equatable | Getting data abstract |  |
| flutter_bloc | State management |  |
| get_it | Component Injector |  |
| getx | Component handling |  |
| pedantic | Code formatting |  |
| rxdart | Data handling async |  |
| logger | Beautiful terminal log |  |
| shared_preferences | Save data local storage |  |
flutter run --flavor developmentYou can choose another flavor staging or production or your custom flavor.
NOTE :
This project is using flutter version 1.22.3 and channel stable
⚠️ If you are get any problem to this project please feel free to create issue
Before we start using patern clean architecture below, we must setting up environment architeture to separate between development, staging, and production part. Ok, let's do it.
In Flutter we separate environment is using flavor, like .env file in react native actualy
We must setting in native code kotlin to make channel called name flavor.
MainActivity.kt
....
import androidx.annotation.NonNull
import io.flutter.embedding.engine.FlutterEngine
import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodChannel
class MainActivity: FlutterActivity() {
private val FlavorChannel = "flavor"
override fun configureFlutterEngine(@NonNull flutterEngine: FlutterEngine) {
super.configureFlutterEngine(flutterEngine)
MethodChannel(flutterEngine.dartExecutor, FlavorChannel).setMethodCallHandler {
call, result ->
result.success(BuildConfig.FLAVOR)
}
}
}
AppDelegate.swift
In ios we must add native code to call the flavor schema in xcode, this is example using swift code.
// flavor
let controller = window.rootViewController as! FlutterViewController
let flavorChannel = FlutterMethodChannel(
name: "flavor",
binaryMessenger: controller.binaryMessenger)
flavorChannel.setMethodCallHandler({(call: FlutterMethodCall, result: @escaping FlutterResult) -> Void in
let flavor = Bundle.main.infoDictionary?["Flavor"]
result(flavor)
})
//!flavorthen don't forget to setup info.plist to make flavor visible when run
<dic>
...
<key>Flavor</key>
<string>$(APP_FLAVOR)</string>
...
</dic>and then setup project from xcode like this.


last part don't forget clone scheme and rename like flavor name.

flavor.dart
class Config {
final String flavorName;
final String apiBaseUrl;
final String apiSentry;
Config({
this.flavorName,
this.apiBaseUrl,
this.apiSentry,
});
static Config _instance;
static Config getInstance({
flavorName,
apiBaseUrl,
apiSentry,
}) {
if (_instance == null) {
_instance = Config(
flavorName: flavorName,
apiBaseUrl: apiBaseUrl,
apiSentry: apiSentry,
);
return _instance;
}
return _instance;
}
}flavor file
import 'config.dart';
class FlavorSettings {
FlavorSettings.development() {
Config.getInstance(
flavorName: 'development',
apiBaseUrl: 'http://dev-url',
apiSentry: 'http://sentry-url',
);
}
FlavorSettings.staging() {
Config.getInstance(
flavorName: 'staging',
apiBaseUrl: 'http://dev-stag',
apiSentry: 'http://sentry-url',
);
}
FlavorSettings.production() {
Config.getInstance(
flavorName: 'production',
apiBaseUrl: 'http://dev-prod',
apiSentry: 'http://sentry-url',
);
}
}Last we call flavor inside main.dart
import module....
///[get debug mode]
bool get isInDebugMode {
bool inDebugMode = false;
assert(inDebugMode = true);
return inDebugMode;
}
void main() async {
/// [Catch some error]
FlutterError.onError = (FlutterErrorDetails details) async {
if (!kReleaseMode) {
FlutterError.dumpErrorToConsole(details);
} else {
Zone.current.handleUncaughtError(details.exception, details.stack);
}
};
/// [run apps] with catch error
runZoned<Future<void>>(() async {
WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized();
Bloc.observer = MyBlocObserver();
await getFlavorSetting();
await di.init();
await disableLendscapeMode();
disableErrorWidget();
runApp(new MyApp());
///[console] flavor running
if (!kReleaseMode) {
final settings = Config.getInstance();
print('🚀 APP FLAVOR NAME : ${settings.flavorName}');
print('🚀 APP API_BASE_URL : ${settings.apiBaseUrl}');
print('🚀 APP API_SENTRY : ${settings.apiSentry}');
}
}, onError: (error, stackTrace) async {
final sentryException = di.sl<SentryException>();
sentryException.reportError(error, stackTrace);
print("❎ ERROR OTHER :$error");
print("❎ STACKTRACE :$stackTrace");
});
}
/// [disable error] widget when [release mode]
void disableErrorWidget() {
if (kReleaseMode) {
ErrorWidget.builder = (details) {
print('Error widget trigerred on :${details.exception}');
print(details.stack.toString());
return Container();
};
}
}
/// [disable landscape] model
Future<void> disableLendscapeMode() async {
await SystemChrome.setPreferredOrientations(([
DeviceOrientation.portraitUp,
DeviceOrientation.portraitDown,
]));
}
///[environment] configuration
Future<FlavorSettings> getFlavorSetting() async {
String flavor =
await const MethodChannel('flavor').invokeMethod<String>('getFlavor');
if (flavor == 'development') {
return FlavorSettings.development();
} else if (flavor == 'staging') {
return FlavorSettings.staging();
} else if (flavor == 'production') {
return FlavorSettings.production();
} else {
throw Exception("Oopss... Flavor name missing");
}
}Sentry's application monitoring platform helps every developer diagnose, fix, and optimize the performance of their code.
import modele....
import 'dart:io';
import 'package:get/get.dart';
import 'package:sentry/sentry.dart';
import 'package:device_info/device_info.dart';
import '../env/config.dart';
Future<SentryEvent> sentryException({
required String loggerType,
required String message,
String? tags,
required dynamic extra,
String? baseUrl,
String? prefix,
String? requestMethod,
String? screen,
required dynamic exception,
}) async {
DeviceInfoPlugin deviceInfo = DeviceInfoPlugin();
late AndroidDeviceInfo androidInfo;
late IosDeviceInfo iosInfo;
if (Platform.isAndroid) {
androidInfo = await deviceInfo.androidInfo;
} else {
iosInfo = await deviceInfo.iosInfo;
}
return SentryEvent(
exception: exception,
logger: loggerType,
environment: Config.getInstance().flavorName,
message:SentryMessage(message),
user: SentryUser(
id: 'id user',
username: 'username',
email: 'email',
extras: extra,
),
breadcrumbs: [
Breadcrumb(
message: loggerType.contains('api') ? 'API Service' : 'UI Lifecycle',
timestamp: DateTime.now().toUtc(),
category: loggerType.contains('api') ? 'api.service' : 'ui.lifecycle',
type: loggerType,
data: loggerType.contains('api')
? {'baseUrl': baseUrl, 'prefix': prefix, 'method': requestMethod}
: {'screen': screen, 'state': 'created'},
level: SentryLevel.info,
)
],
contexts: Contexts(
operatingSystem: SentryOperatingSystem(
name: Platform.isAndroid ? 'Android' : 'IOS',
version: Platform.isAndroid
? androidInfo.version.toString()
: iosInfo.systemVersion,
build: Platform.isAndroid ? androidInfo.model : iosInfo.model,
kernelVersion:
Platform.isAndroid ? androidInfo.hardware : iosInfo.utsname.version,
rooted: false,
),
app: SentryApp(
name: 'Name of Apps',
version: '1.0.0',
identifier: 'com.apps.module',
buildType: 'release',
startTime: DateTime.now().toUtc(),
),
device: SentryDevice(
name: Platform.isAndroid ? androidInfo.product : iosInfo.name,
family: Platform.isAndroid
? androidInfo.manufacturer
: iosInfo.identifierForVendor,
model: Platform.isAndroid ? androidInfo.model : iosInfo.model,
modelId: Platform.isAndroid ? androidInfo.id : iosInfo.utsname.nodename,
arch:
Platform.isAndroid ? androidInfo.hardware : iosInfo.utsname.machine,
brand: Platform.isAndroid ? androidInfo.brand : iosInfo.name,
manufacturer: Platform.isAndroid
? androidInfo.manufacturer
: iosInfo.utsname.machine,
screenResolution: '${Get.width.toInt()} x ${Get.height.toInt()}',
),
),
);
}The Dependency Rule Source code dependencies only point inwards. This means inward modules are neither aware of nor dependent on outer modules. However, outer modules are both aware of and dependent on inner modules. Outer modules represent the mechanisms by which the business rules and policies (inner modules) operate. The more you move inward, the more abstraction is present. The outer you move the more concrete implementations are present. Inner modules are not aware of any classes, functions, names, libraries, etc.. present in the outer modules. They simply represent rules and are completely independent from the implementations.
In some case we cannot implementation code by theary and just reading some tutorial without complete code. So here we go, I was build some code and improve some code from some tutorial and make it better I think :), I hope in this part can help us to make some simple Boilerplate.
This is part more easy to handling some data error from network or other.
abstract class UseCase<Type, Params> {
Stream<Either<Failure, Type>> build(Params params);
Stream<Either<Failure, Type>> execute(Params params) {
return build(params).onErrorResume((error) {
print("error from streams : $error");
Failure failure;
if (error is Failure) {
failure = error;
} else if (error is DioError) {
failure = ServerFailure(message: error.message);
} else {
failure = AnotherFailure(message: "$error");
}
return Stream.value(Left(failure));
});
}
}
class NoParams extends Equatable {
@override
List<Object> get props => [];
}In this part we are enable to make option where data come from local or network
abstract class BaseDataSourceFactory<T> {
T createData(DataSourceState dataSourceState);
}
enum DataSourceState { network, local }class BindingDataSourceFactory
extends BaseDataSourceFactory<BindingDataSource> {
BindingRemote _bindingRemote;
BindingLocal _bindingLocal;
BindingDataSourceFactory({
@required BindingRemote bindingRemote,
@required BindingLocal bindingLocal,
}) : _bindingRemote = bindingRemote,
_bindingLocal = bindingLocal;
@override
BindingDataSource createData(DataSourceState dataSourceState) {
switch (dataSourceState) {
case DataSourceState.network:
return _bindingRemote;
break;
case DataSourceState.local:
return _bindingLocal;
default:
throw UnsupportedError(
'DataSourceState $dataSourceState is not applicable in BindingDataSourceFactory');
}
}
}Internationalization is the design and development of a product, application or document content that enables easy localization for target audiences that vary in culture, region, or language. Internationalization is often written in English as i18n, where 18 is the number of letters between i and n in the English word
In this part we must handling component string and prepare if our project is using multiple language (in this case usin US and ID)
//NOTE : base translation class
abstract class Translation {
String get msgEmailInUse;
String get msgInvalidCredentials;
String get msgInvalidField;
String get msgRequiredField;
String get msgUnexpectedError;
String get addAccount;
String get confirmPassword;
String get email;
String get enter;
String get login;
String get name;
String get password;
String get reload;
String get wait;
}
//NOTE : implement to language class
class ID implements Translation {
String get msgEmailInUse => 'Email sudah digunakan';
String get msgInvalidCredentials => 'Username atau password salah.';
String get msgInvalidField => 'Bidang tidak valid';
String get msgRequiredField => 'Kolom yang harus diisi';
String get msgUnexpectedError => 'Ada yang salah. Silahkan coba lagi nanti.';
String get addAccount => 'Buat sebuah akun';
String get confirmPassword => 'Konfirmasi sandi';
String get email => 'Email';
String get enter => 'Gabung';
String get login => 'Login';
String get name => 'Nama';
String get password => 'Kata sandi';
String get reload => 'Muat ulang';
String get wait => 'Tunggu...';
}
class R {
static Translation string = ID();
static void load(Locale locale) {
switch (locale.toString()) {
default:
string = ID();
break;
}
}
}
example calling :
R.string.msgEmailInUse
output :
Email sudah digunakan
This architecture is made with love:blush: and more things using great tutorials by great people, please visit this project credit, thank you.
Happy codding 🖤
Flutter Community
Filled stack
Reso Coder
Rezky Aulia Pratama
Ashish Rawat