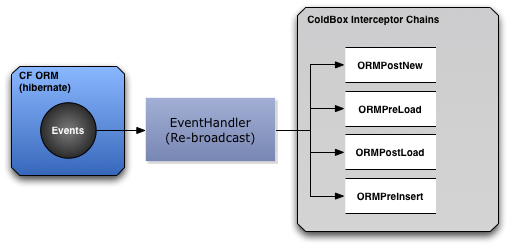
Hibernate can announce events to listener objects so they can tap in to the life-cycle of the entities. You can either listen to the events globally or within the entity itself by just declaring a few listener methods. The cborm module taps in to the global Hibernate events and re-transmits them as ColdBox interception points. This allows you to intercept ORM events via multiple CFC listeners instead of the rigid approach of a single listener CFC which the ColdFusion engines give you.
This is achieved by the cborm.models.EventHandler class and by telling the application about it. The event handler also (if configured) will talk to WireBox and auto wire entities with dependencies. Just add your dependency injection properties and off you go with entity injection.
You can enable the cborm event handler by opening the Application.cfc and adding two settings:
eventHandlingeventHandler
{% code title="Application.cfc" %}
this.ormSettings = {
cfclocation="model",
dbcreate = "update",
dialect = "MySQLwithInnoDB",
logSQL = true,
// Enable event handling
eventhandling = true,
// Set the event handler to use, which will be inside our application.
eventhandler = "cbmorm.models.EventHandler"
};{% endcode %}
That's it, now the cborm event handler will listen to the ORM events, re-broadcast them and you can create ColdBox Interceptors to listen to them.
Below are the new interception points the ORM Event Handler exposes with the appropriate interception data it announces. Just create an Interceptor CFC, add the method with the name of the interception point and off you go!
| Interception Point | Intercept Structure | Description |
|---|---|---|
ORMPostNew |
{entity} |
Called via the postNew() event |
ORMPreLoad |
{entity} |
Called via the preLoad() event |
ORMPostLoad |
{entity} |
Called via the postLoad() event |
ORMPostDelete |
{entity} |
Called via the postDelete() event |
ORMPreDelete |
{entity} |
Called via the preDelete() event |
ORMPreUpdate |
{entity,oldData} |
Called via the preUpdate() event |
ORMPostUpdate |
{entity} |
Called via the postUpdate() event |
ORMPreInsert |
{entity} |
Called via the preInsert() event |
ORMPostInsert |
{entity} |
Called via the postInsert() event |
ORMPreSave |
{entity} |
Called via the preSave() event |
ORMPostSave |
{entity} |
Called via the postSave() event |
ORMPreFlush |
{entity} |
Called before the Hibernate session is flushed. Triggered via the preFlush() event |
ORMPostFlush |
{entity} |
Called after the Hibernate session is flushed. Triggered via the postFlush() event |
With the exposure of these interception points to your ColdBox application, you can easily create decoupled executable chains of events that respond to ORM events. This really expands the ORM interceptor capabilities to a more decoupled way of listening to ORM events. You can even create different interceptors for different ORM entity classes that respond to the same events, extend the entities with AOP, change entities at runtime, and more; how cool is that.
component extends="coldbox.system.Interceptor"{
function ORMPostLoad( event, interceptData, rc, prc ){
// audit the data.
var state = interceptData.entity.getMemento();
autidService.logState( state, interceptData.entity );
}
}